Certificates and Benefits of Our Manuka Honey
Each batch of our honey undergoes independent laboratory testing in New Zealand, carried out by the accredited Analytica Laboratories.
Why care about certificates?
→ A certificate guarantees not only the authenticity of the honey but also the concentration of key active compounds that determine its potency, quality, and health benefits.
Below you’ll find a clear breakdown of all the certificates – plus a translation from “science speak” into plain English. 😉
What will you find here?
- The certificates themselves – preview images and full PDF versions.
- A clear summary table with the main values, so you don’t have to decipher the full certificates.
- Explanation of key parameters – what they mean, their values, and how they benefit you.
- A comparison of our different Manuka honeys and what the measured values say about them.
↓ At the bottom of this page, you’ll find a table with all 10 tested parameters along with brief explanations in plain English.
Certified Parameters – Summary
- The table has multiple columns. On mobile, swipe sideways to view the full table! 👉
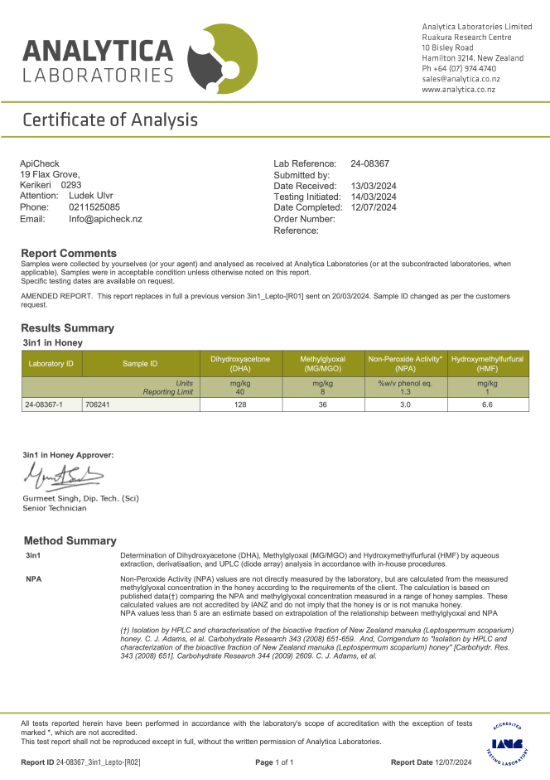
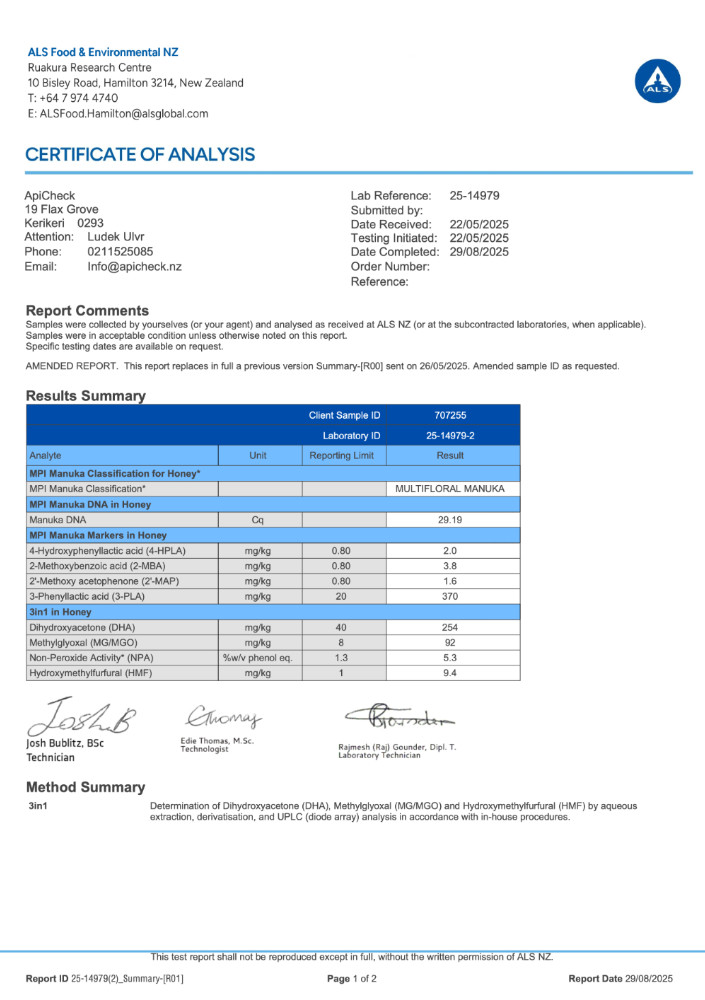
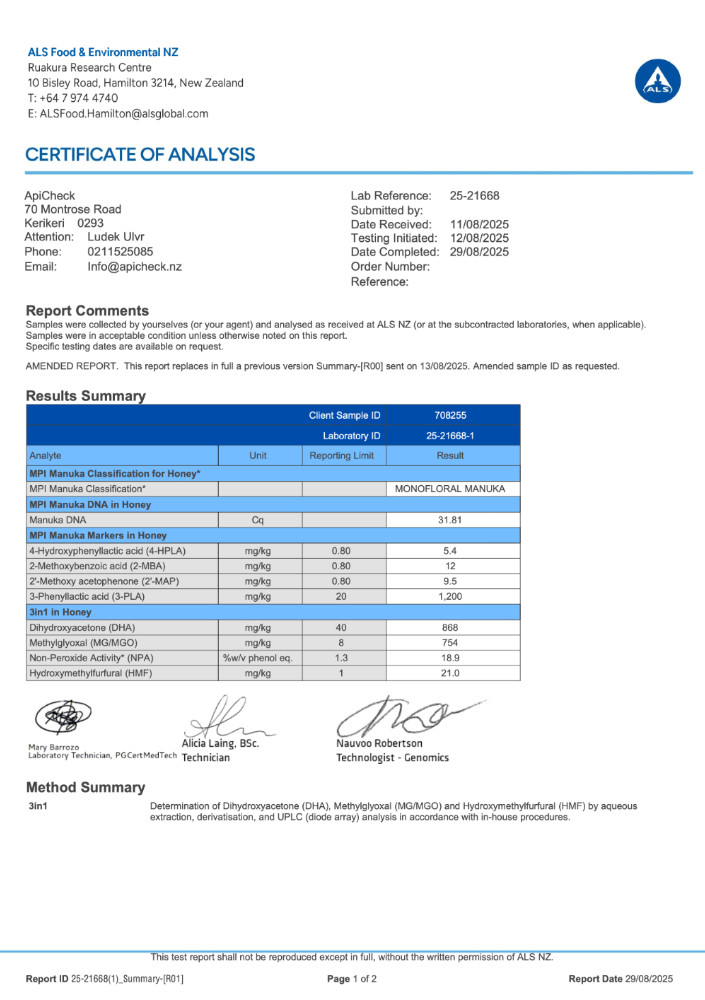
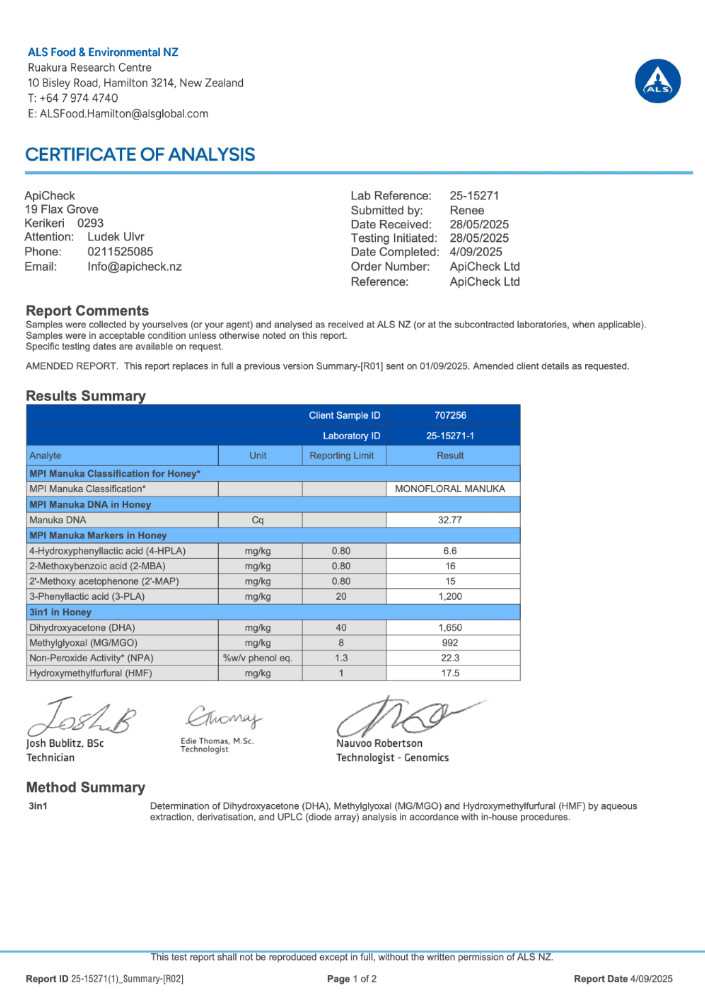
| Tested Honeys | MGO (mg/kg) | NPA | DHA (mg/kg) | HMF (mg/kg) | 3-PLA (mg/kg) | Classification |
| Manuka 90+ MGO | 92 | 5.3 | 254 | 9.4 | 370 | Monofloral |
| Manuka 514+ MGO | 754 | 18.9 | 868 | 21.0 | 1200 | Monofloral |
| Manuka 829+ MGO | 992 | 22.3 | 1650 | 17.5 | 1200 | Monofloral |
| Multiflora 30+ MGO | 36 | 3.0 | 128 | 6.6 | – | Multifloral |
Whether a honey is classified as pure Manuka (monofloral) or a Multiflora (multifloral) is determined by four key markers set by the New Zealand government. One of these is 3-Phenyllactic acid (abbreviated as 3-PLA).
We explain the remaining markers from the table below. ↓
Key substances in Manuka
Overall Strength 💪
Substance: Methylglyoxal
Abbreviation & Unit: MGO (mg/kg)
The main active compound in Manuka honey. The higher the number, the stronger the effects.
How methylglyoxal helps:
- Soothes sore throat and reduces inflammation.
- Supports healthy digestion.
- Acts against bacteria and fungi.
- Promotes wound healing.
Antibacterial Effect 🧴
Substance: Non-Peroxide Activity
Abbreviation & Unit: NPA (% phenol equivalent)
Represents the antibacterial power converted to the strength of a common disinfectant (phenol).
- NPA 10+ = strongly antibacterial.
- NPA 20+ = very strong, suitable even for therapeutic use.
Future Potency 🌿
Substance: Dihydroxyacetone
Abbreviation & Unit: DHA (mg/kg)
Naturally present in the nectar of the Manuka bush. During honey maturation, it transforms into MGO.
- Higher DHA = potential for greater effectiveness over time (“matures” after harvest).
Honey Freshness 🌸
Substance: Hydroxymethylfurfural
Abbreviation & Unit: HMF (mg/kg)
Forms when honey is overheated or stored too long.
- Low value = fresh and properly stored honey.
The parameters above show how potent, pure, and fresh the honey is. → A certificate isn’t just a stamp — it gives a detailed picture of what Manuka can truly do for you. ✓
What do the values from the certificate table tell us about our honeys?
🍯 Manuka 90+ MGO
- MGO 92 mg/kg – mild to moderate antibacterial strength. Great for daily immune support.
- NPA 5.3 – decent value for an entry-level Manuka. Strong therapeutic effects usually start at 10+.
- DHA 254 – solid value (MGO levels will rise).
- HMF 9.4 – absolutely fine. Indicates the honey is fresh and properly stored.
- 3-PLA 370 – confirms it’s a pure Manuka honey.
🔹 Summary: Ideal for daily use and boosting your natural immunity. Note that the actual MGO content is more than double the declared value.
🍯 Manuka 514+ MGO
- MGO 754 mg/kg – strong antibacterial activity, reaching therapeutic levels. Great for digestive issues, colds, or wound care.
- NPA 18.9 – excellent value, reflects strong antibacterial strength (anything over 10+ is considered powerful).
- DHA 868 – high natural base for future MGO development.
- HMF 21.0 – within acceptable limits (up to 40 is OK), although lower would be better.
- 3-PLA 1200 – exceptionally high Manuka content. Confirms monofloral quality.
🔹 Summary: A high-strength Manuka. Suitable as support during colds or other health issues.
🍯 Manuka 829+ MGO
- MGO 992 mg/kg – exceptionally strong honey, ideal for serious concerns like weakened immunity, infections, or poor wound healing.
- NPA 22.3 – outstanding value. Equivalent to medical-grade honey used in wound treatment.
- DHA 1650 – extremely high natural base. MGO content will continue to increase over time.
- HMF 17.5 – very low, indicating extremely fresh and carefully handled honey.
- 3-PLA 1200 – confirms the highest purity and Manuka concentration.
🔹 Summary: Exceptionally potent Manuka honey – for customers seeking the most powerful product nature can offer. Highly effective.
🍯 Multiflora 30+ MGO
- MGO 36 – suitable for everyday enjoyment..
- NPA 3.0 – a lower value, as expected from a blend of different floral sources.
- DHA 128 – lower compared to pure Manuka honeys.
- HMF 6.6 – exceptionally low. Indicates extremely fresh and well-stored honey.
🔹 Summary: A blend of Manuka and other New Zealand floral nectars. While the MGO, NPA, and DHA values are lower than in pure Manuka, it still offers verified benefits.
Final Step
Now you know everything there is to know about our honey. Ready to experience its benefits for yourself? Go for it!
→ TASTE IT ✓
Supplementary Table
In the table below, you’ll find additional parameters listed in the certificates – along with explanations, benefits, and typical values.
| Parameter Name | What It Means | Why It Matters |
| MPI Manuka Classification | Official classification of Manuka honey as monofloral or multifloral. | Indicates whether the honey is predominantly made from Manuka nectar (monofloral = stronger and more valuable). |
| Manuka DNA (Cq) | Value from a PCR test showing the amount of Manuka pollen DNA in the honey. | The lower the number (below 36), the higher the Manuka content – crucial for recognition as genuine Manuka honey. |
| 4-HPLA | One of the 4 marker compounds characteristic of Manuka. | Used to verify the authenticity and botanical origin of the honey (only present in Manuka nectar). |
| 2-MBA | The second of four compounds used to identify true Manuka. | Helps officially confirm that the honey is from Manuka blossoms. |
| 2′-MAP | The third marker compound naturally occurring in Manuka honey. | An important part of the official NZ Ministry for Primary Industries classification. |
| 3-PLA | The fourth key compound, used to distinguish between mono- and multifloral honeys. | Confirms a high share of Manuka nectar – important for purity and strength. |
| DHA (Dihydroxyacetone) | Compound from fresh Manuka nectar that naturally converts to MGO. | Indicates future potency – the higher the DHA, the better. |
| MGO (Methylglyoxal) | Main antibacterial compound in Manuka honey. | Determines the strength of the honey. MGO 100+ is basic; 800+ is very strong and therapeutic. |
| NPA (Non-Peroxide Activity) | Antibacterial potency converted to phenol equivalent strength. | NPA above 10 is considered very strong – the value correlates with MGO content. |
| HMF (Hydroxymethylfurfural) | Compound that forms when honey is overheated or aged. | The lower the value, the fresher and more gently processed the honey. Below 40 mg/kg is acceptable. |